ChatGPT or human author?
Fraunhofer SIT Researches Automated Recognition Capabilities
Whether application letters, school essays, exams or program codes - with the text AI ChatGPT, texts of all kinds can be generated automatically within seconds. This works sometimes more, sometimes less well - and humans often fail to reliably classify the result as AI-generated or human-written.
ChatGPT text recognition with authorship verification
Fraunhofer SIT is researching ways to help recognize texts created with ChatGPT. Among other things, our text forensic experts work with a self-developed method for authorship verification, COAV: Originally, it was used to detect plagiarism in scientific papers, for example. Since COAV compares texts on a stylistic basis, this method can also be used to identify a specific "author," namely ChatGPT. This is used to calculate the distances between texts using similarities of text modules and typical consecutive letter strings: Is the text closer to GPT or closer to a human?
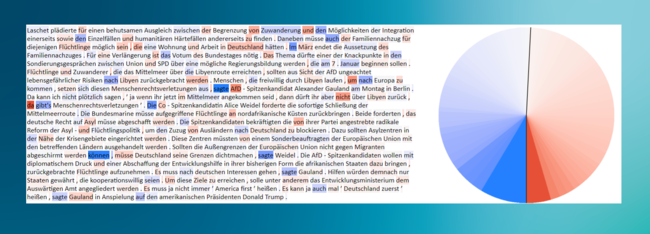
Our IT forensics expert Lukas Graner (dept of IT forensics) has demonstrated this using news texts as an example: He had existing online messages written by (human) journalists reworded via ChatGPT and tested them with the tool. Text passages marked in blue indicate that they are more likely to have been written by a human, while red markings stand for ChatGPT.
The graphics clearly show the result: In the first case, you see an excerpt from a news text from the Süddeutsche Zeitung with markings - added up in the result chart, you see that the blue portion predominates. The result: A human being probably wrote this text.
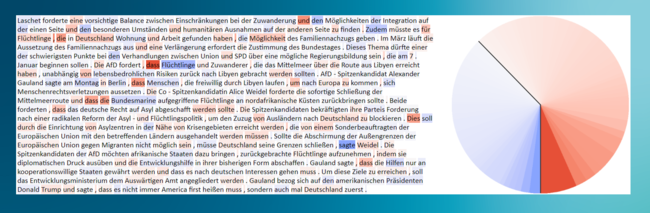
For the second example, the message text from ChatGPT was rephrased with our own stylistic preferences and then tested with COAV. The result shows: This text was created by machine.
Other methods of ChatGPT text detection
There are other research approaches in text forensics that are looking at how to get to the bottom of ChatGPT texts - again using automated AI tools. For example, there are
- GPT Zero: an app developed by a computer science student at Princeton University (https://gptzero.me/)
- DetectGPT: a web app that is still in the experimental phase, the paper can be found here: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2301.11305v1.pdf)
- Watermarking for Large Language Models: A proposal from researchers at the University of Maryland - they show how digital watermarks can be woven into machine-generated texts so that it can be directly indicated that this is an AI text that was created without human help. https://deepai.org/publication/a-watermark-for-large-language-models
An overview of other tools can be found on the SEO.AI website, which also regularly updates its list.
However, you should not blindly trust the technology when it comes to recognition tools, but also take a critical look at them. This is because the tools never work 100 per cent reliably, there is always a false positive rate that incorrectly classifies texts as AI-generated; or the reverse case, where AI texts are not recognised as such. Due to low recognition rates, Open AI has taken its own AI text recognition service offline again: "As of July 20, 2023, the AI classifier is no longer available due to its low rate of accuracy." (LINK)
Examiners at universities and teaching staff at schools should therefore never rely completely on an AI text recognition tool. However, it can serve as an initial indicator of which examinees or students should possibly have a discussion about the content of the written text.
Confusion with plagiarism detection
AI text recognition tools should not be confused with plagiarism detection. There have long been tools that can recognise plagiarism, i.e. when texts are copied from sources and not referenced. These have very high detection rates as they work in a completely different way. They work with sequences of cryptographic hashes, which are very reliable. In the case of long passages and a match, plagiarism can be safely assumed.
